Honestly, when thinking about car makers clean technologies and sustainability aren’t the first thoughts that come into someone’s mind. But times are changing!
Besides some efforts in the development of hybrid or full electric cars, currently numerous car producers switch to the implementation of bioplastics into their vehicles and additionally explore the chances of different kinds of biofuels. This is not just to improve their image, but mainly for economic reasons. As the price for crude oil rises, and consequently the prices of products derived thereof rise too, a technically and economically viable alternative is required.
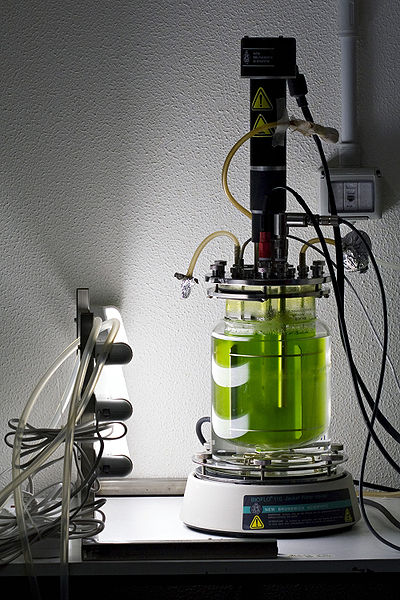
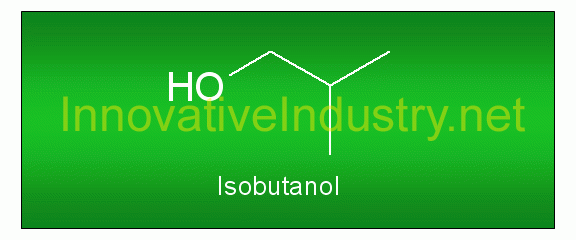
Scientists of the American car manufacturer Ford Motor Company are investigating the suitability of renewable resources such as algae as potential automotive fuels. At present, research is predominantly about finding economical paths to cultivate high oil producing algae for large scale industrial production. As this is still a challenge, Ford promises to promote strategies to produce biodiesel from algae oil. For the near future bioethanol and biobutanol – alcohols derived from cellulosic feedstocks – seem to have greater potential and hence, are subject of Ford’s research. The company is also a pioneer in using green materials, mostly soy based polyols called soy-foam, within its cars. At this moment, there it is a growing interested in using a wood-fiber-filled polymer provided by Solegear, a Canadian green chemistry start-up. This biopolymer (Traverse) can be blended with fossil polymers and is intended for the production of partially biodegradable steering wheels. There is no reason to worry about car parts breaking down in heat or coming apart in their hands since such bioplastics decompose only under catalytic processes in commercial compost environments.
While many other companies within the automotive industry are just discussing the possible substitution of conventional plastic with biobased materials, one of the biggest car producers – the Japanese Toyota Motor Corporation – is going a few steps further. The car manufacturer does not only use bioplastics like PLA (polylactic acid) for essential parts of their vehicles, but it also started to produce them. Since it became obvious that the time for petroleum based materials will soon be over and the demand of alternatives increases, Toyota got involved into the development and the biotechnological production of PLA.
In addition to the company’s ambition in PLA another semi-bioplastic is promoted and will be used to substitute fossil plastic. Bio – PET (bio – polyethylene terephthalate) will be introduced into the luggage compartment liner in the Lexus “CT200h” at the beginning of 2011. This hybrid plastic covers 80 % of the interior surfaces of the new Lexus. Traditional polyethylene terephthalate; consists of 70% terephthalic acid and 30% monoethylene glycol. Bio – PET is made by replacing monoethylene glycol with a biological feedstock derived from sugar cane.
Not just the companies mentioned above focus their efforts to change to clean tech materials. Meanwhile, quiet a number of car producers mix, modify and optimize green polymers to fit their need. Mitsubishi in cooperation with Aichi Industrial Technology developed Bio – PBS (bio – polybutylene succinate) which is strengthened by bamboo fibers. PBS is made from succinic acid and 1,4 butandiol. The succinic acid derives by the fermentation of sugar or corn.
Tire manufacturer Goodyear uses BioTRED which contains a significant corn derived component. BioTRED is used as a filling material in the production of tires.
Mazda announced the development of a heat resistant hybrid biopolymer containing 88 % PLA and 12 % fossil based additives. This material is employed in the Mazda “Premacy Hydrogen RE Hybrid”.
For sure, these companies are not the only ones who explore the potential of bioplastics. Many others are on the road to sustainability too. Within the next years the automotive industry has to switch to clean tech products to stay competitive. Surprisingly, just American and Asian car producers are known for their switch to clean / green materials. During the research for this article not one European company appeared. Do they keep it all secret or do they ignore the signs of time?
In view of changing conventional feedstocks for polymers and fuels to sustainable and biobased raw materials such efforts are vital. Although, this is just the beginning of a tremendous modification in industrial production, it’s fundamental not just to demand clean tech solutions but moreover to support these progressing technologies by buying them.
Update February 2011: a related post about Cars Made From Renewable Materials has been published!